On September 25th, 2019, Nigeria conducted the first trial of the (5G) fifth-generation cellular networks.
What is 5G?
5G is the fifth-generation technology standard for broadband cellular networks. It is the upgrade of the 4G (fourth generation) cellular networks. 5G promises faster data transmissions than all the other generations of cellular networks, delivering up to 20 Gigabits-per-second. 5G also offers lower power consumption, lower latency, improved security, reliability, and availability.
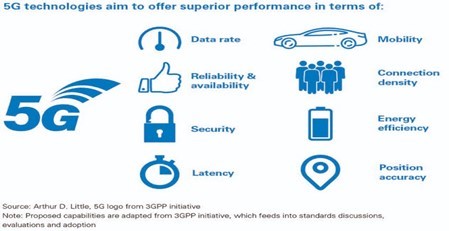
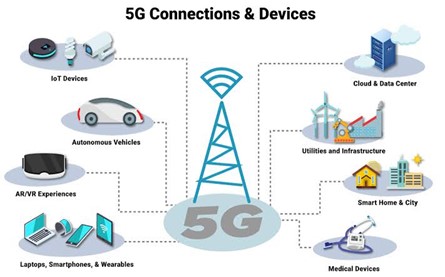
These capabilities promise to bring out the full potential of IoT (Internet of Things) and more interconnections between devices.
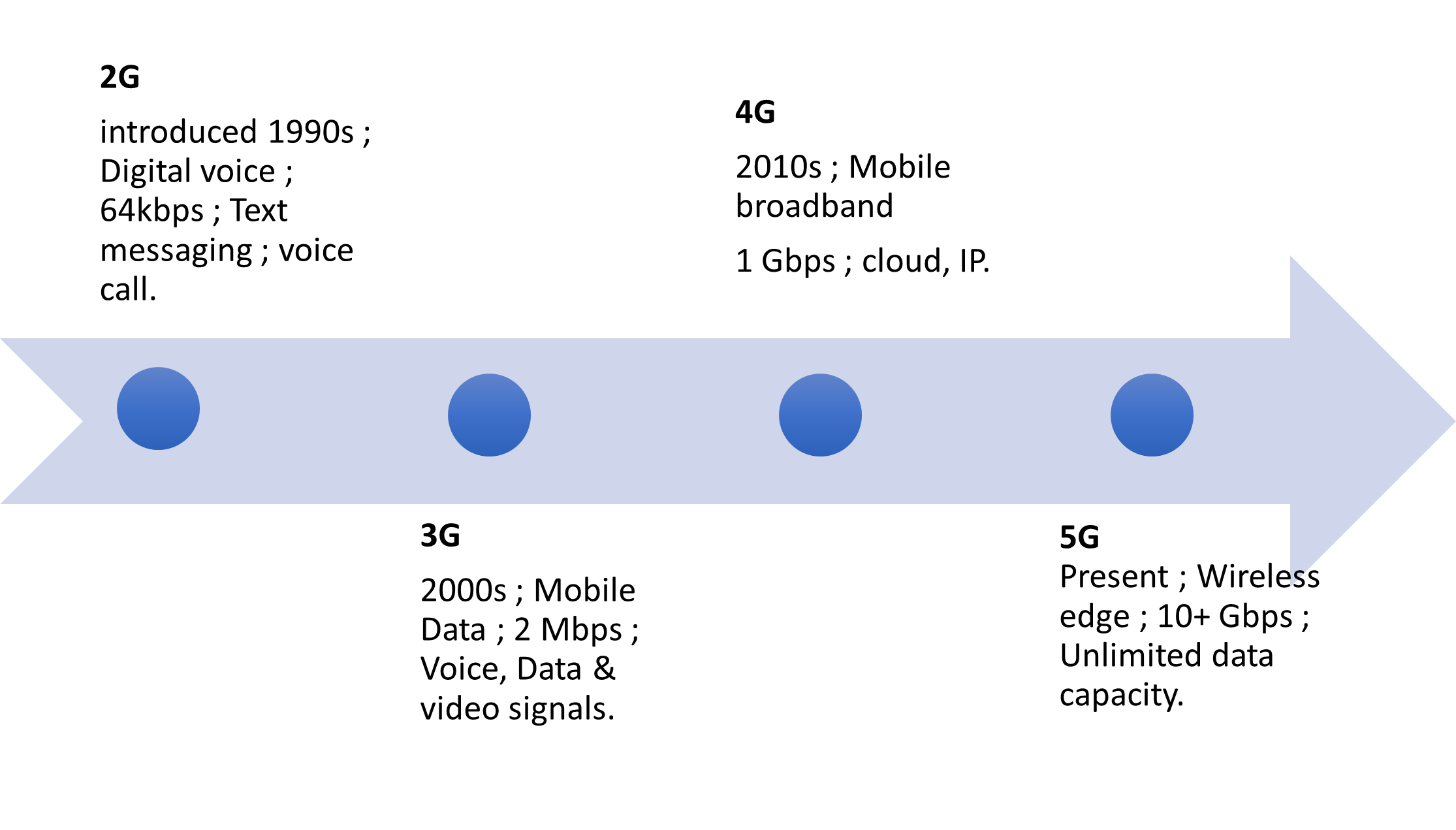
5G vs the older generations.

Evolution of the cellular networks
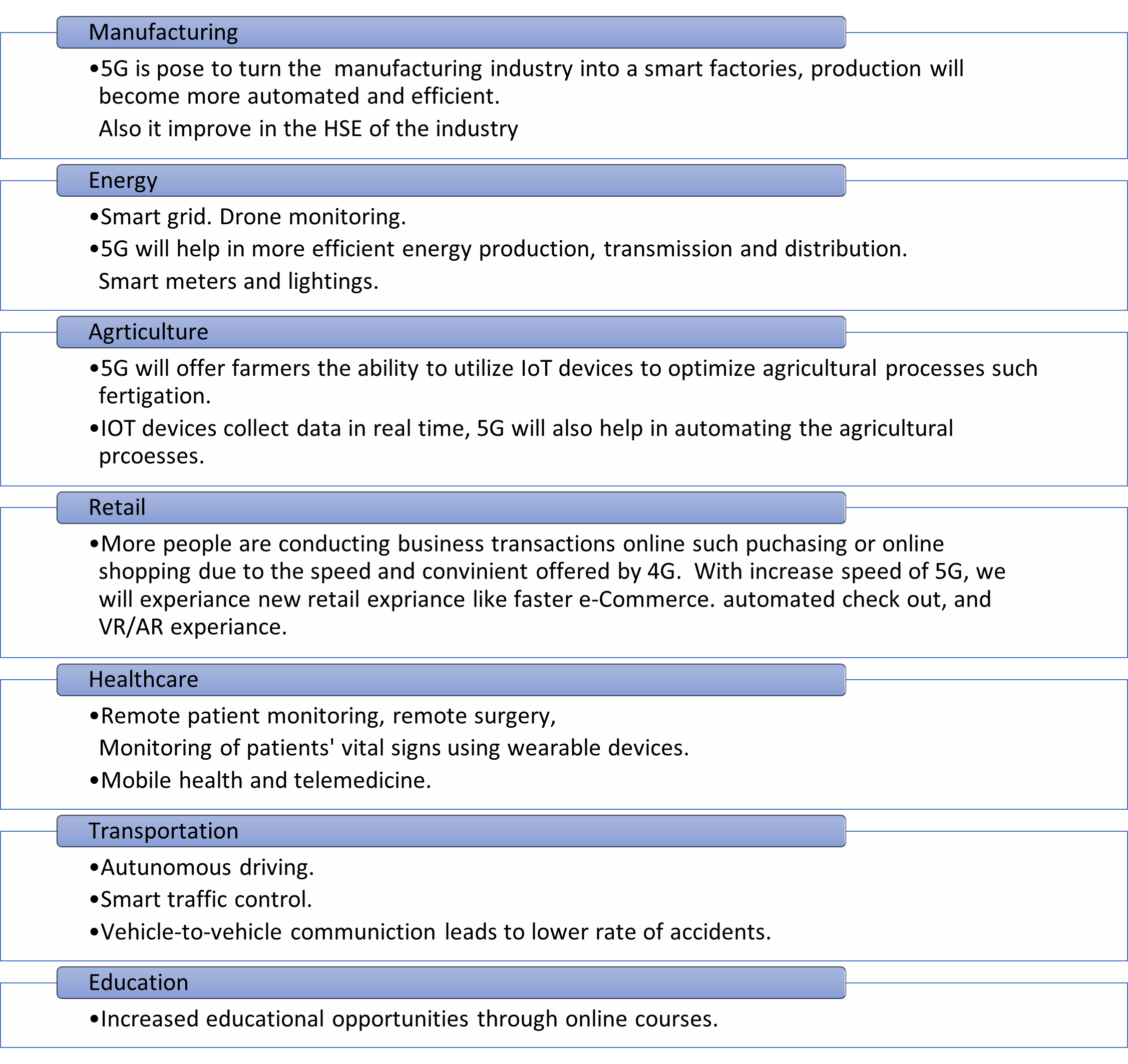
Industries to benefits from 5G
Deployment of 5G will set the stage for new opportunities across many industries such as:
5G Security Risks.
Unlike the older generations of the cellular network standards that are mostly hardware-based architecture, 5G technology is predominantly software-based. Just like all other software-based systems, 5G technology is not a risk but it has vulnerabilities.
- Vendor Software compromise: 5G relies on software, this software is designed by vendors. The vendor may intentionally hide a vulnerability in the software design that can be exploited later by the vendor. The case in point the Huawei versus the US government.
- Accessibility compromise: Access disruption is one area that is of concern. Again, Due to it dependent on software, this gives an attacker the chance to propagate his malware to multiple access points in very little time. The attacker can take the whole network offline resulting in lost connectivity and major disruption. Disruption of key sectors like Defence might have a major implication on a state’s security.
- Data compromise: 5G offers the avenue for more integration of devices thereby increasing the amount of data transmission and these devices has the ability to store some level of data. An attacker who may gain access to the device later will have access to such sensitive information.
- High bandwidth: ironically, high speed offered by 5G technology has its own associated risks, the speed offers less time for compromise and transfer of data. Most cybersecurity solutions detect attack incidents based on changes in traffic flow in a network. The speed offers an attacker less time to get in and get out before any monitoring solutions detects.
- Number of the transmitters and devices. 5G requires more numbers of transmitters than the older generation cellular networks because 5G uses higher frequency. in telecommunication higher frequencies means faster data transmission but also coverage. This increase in transmitters and interconnected devices create much larger attack surface thereby increasing the potential targets. An attack on one device can compromise the whole network. This increases the burden of securing more targets.
Conclusion
5G is a relatively new technology, it has a lot of benefits so also associated risks. It requires a new cyber security approach. An approach that will cover all the billion devices estimated to connect.
Certfort Ltd Professional Services to 5G deployment.
Certfort is an ICT organisation with highly experienced professionals that can help provide services that can assist clients to manage the risks involved in the adoption of 5G, such as:
- Help client achieve a level of compliance on the 5G related international standards
- Perform Research: research on the risk associated with the specific vendors tools in the market and also inform a client on which vendors to avoid.
- Provide Products such as in-built anti-malware tools.
- Provide endpoint protections services/tools that will cover all the connected device including the BYODs.

